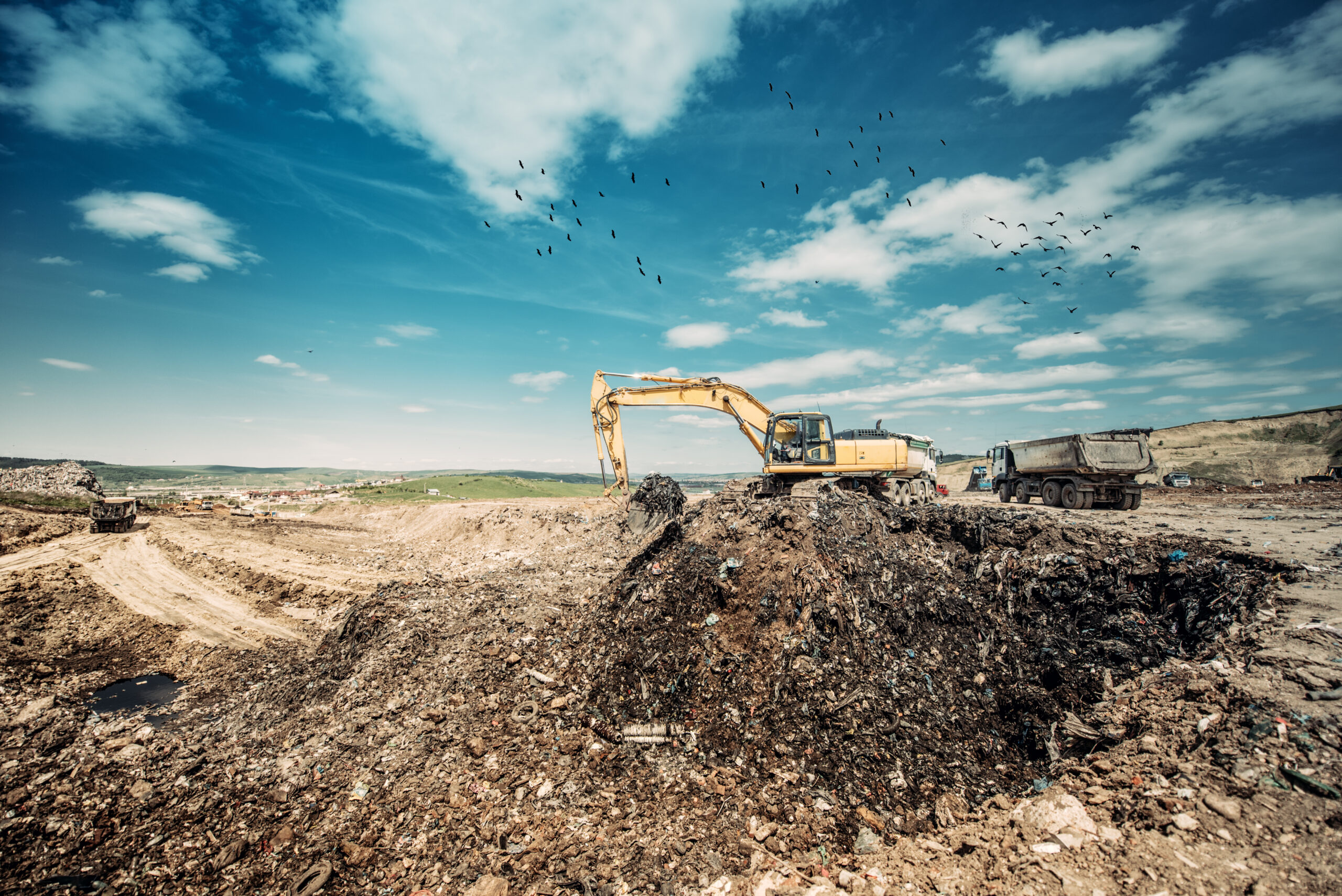
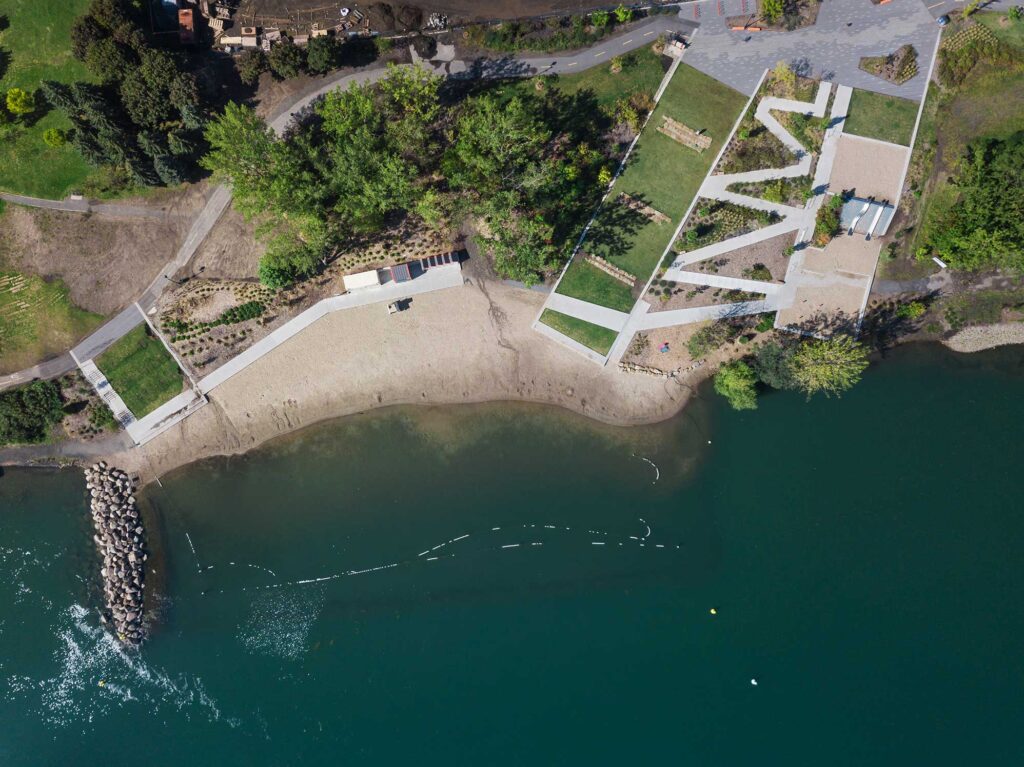
Hébertville Technical Landfill Site
Hébertville Technical Landfill Site
2022
Municipal

The Régie des matières résiduelles du Lac-Saint-Jean entrusted gbi with multiple major mandates aimed at optimizing, expanding, and ensuring the long-term sustainability of the Hébertville Technical Landfill Site (LET). These complementary mandates have helped ensure regulatory compliance, improve operational performance, and significantly extend the site’s lifespan while minimizing environmental and community impacts.
gbi’s interventions focused on two main areas:
- Design and construction of new landfill infrastructure, including new cells and the final capping of existing cells.
- Long-term site planning, through the completion of an environmental impact study for landfill expansion.
Environmental Impact Study and Landfill Expansion Planning

To meet the region’s long-term waste disposal needs, gbi also conducted the environmental impact assessment for the Hébertville-Station landfill expansion.
This strategic mandate ensured the development of the site over a projected 40-year horizon.
- Analysis of six potential expansion zones, leading to selection of the optimal area;
- Assessment of environmental, geographical, ecological, social, and economic impacts;
- Stakeholder consultations and participatory processes;
- Development of mitigation measures, monitoring, and environmental follow-up programs;
- Submission of the study to the Ministry of Environment, Fight Against Climate Change, Wildlife and Parks (MELCCFP).
The expansion is planned in two phases: Phase 1 adds new cells to the existing area, and Phase 2 involves a potential 25-hectare extension to be constructed progressively according to site needs.
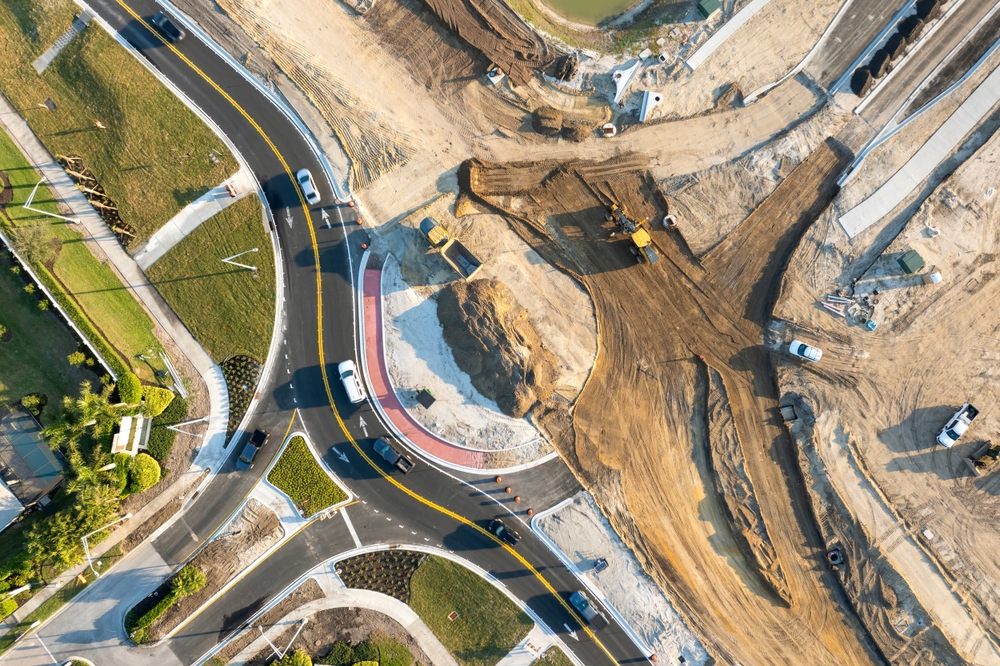
Landfill Cell Construction and Rehabilitation
As part of Phase 3 of the site, gbi was responsible for constructing two new landfill cells and performing the final cover of three existing cells.
The works aimed to ensure landfill impermeability, optimize leachate and biogas management, and guarantee the safety and durability of the infrastructure.
- Rock blasting, crushing, and management of excavated material;
- Construction of multilayer impermeability systems using geosynthetics for both new and final cover cells;
- Installation and connection of leachate collection and drainage networks;
- Installation of biogas capture systems, including active wells, geodrains, and integration with existing networks;
- Slope grading, stormwater management, and profile compliance;
- Extension and modification of the operational access road to facilitate safe movement of heavy equipment.
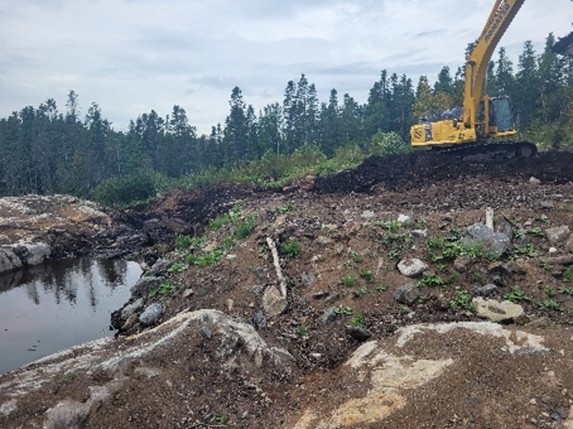

Site Complexity and Key Challenges
The project was carried out in a technically and environmentally demanding context. The presence of shallow bedrock required blasting, crushing, and careful management of excavated materials. The biogas collection systems had to be adapted during construction to ensure proper integration with existing infrastructure and to reflect site-specific conditions observed in the field. Managing slopes and access roads was also a key challenge in order to ensure safe operations and efficient circulation of heavy equipment.
Lastly, the environmental sensitivity of the site required particular attention, including the protection of wetlands and the mitigation of nuisances such as noise, dust, and traffic.
Innovations et initiatives durables
The project stood out through the integration of biogas collection networks from previous phases, ensuring continuity and optimization of existing systems. The reuse of all excavated materials generated on site significantly reduced the need for imported materials and road transportation, thereby lowering the project’s environmental footprint. To further limit impacts on the surrounding community and environment, blasting activities were scheduled outside peak tourist periods.
In addition, optimization strategies were proposed to extend the site’s operational lifespan, including improved waste compaction, the implementation of organic waste collection, and the development of circular economy initiatives.
Professional Services Provided by gbi
- Feasibility studies
- Overall site design and planning
- Cost estimates and scheduling according to work phasing;
- Environmental and regulatory studies
- Preliminary and final plans and specifications
- Assistance during tendering processes
- Bid analysis
- Stakeholder coordination
- Office supervision and quality control
- On-site supervision for Cell 7, partial construction of Cell 9, and final capping of Cells 2, 3, and 4